NON-STOP™
Annual Down-Time as Low as 0.5%!
Unscheduled down-time can be a major headache, but is often a necessary evil.
How do you get Real reliability without breaking the bank?
01
Based on Japanese Technology
Pursuit of Excellence
The Japanese, as a people, is relentless in pursuing the holy grail of Zero Defects and making their products last a VERY long time.
A team of Japanese technical experts used their know-how to create the technology that we now simply call: Non-Stop™.
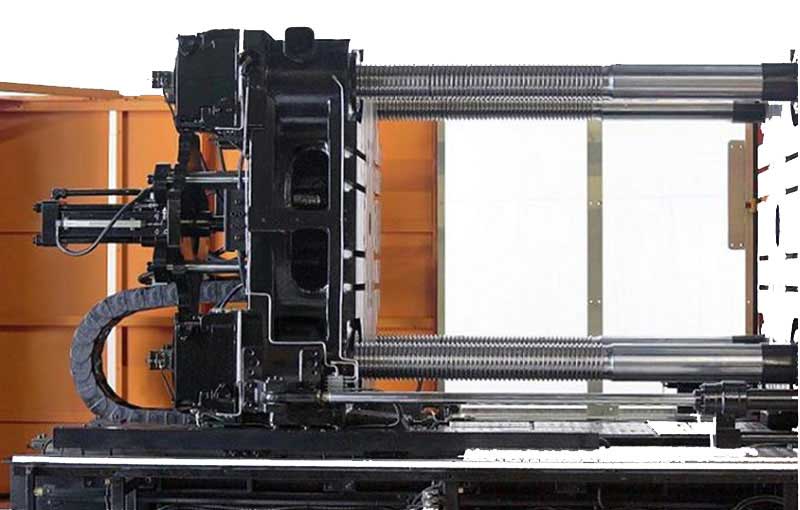
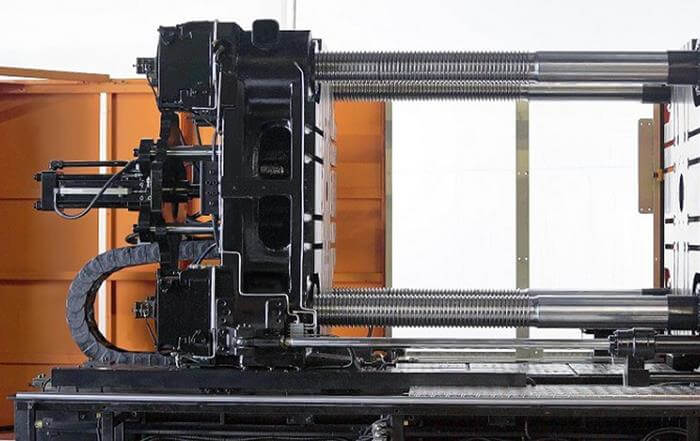
Two-Platen
Available first on the 2nd-Generation Two-Platen machines. Other machine models will follow.
02
Precision Hydraulics™
Foundations of Reliability
The philosophy of Not-Making-Things-Worse is the cornerstone of achieving great reliability — that means reducing unnecessary wear-and-tear whenever possible.
Smooth as Silk
Hydraulics systems relentlessly fine-tuned and optimized by European and Japanese experts to minimize pressure drops and eliminate spikes and over-shoots turn all mechanical motions to silky smoothness.


03
Rock Solid Machanics
Designed Robustness
Patented mechanical designs have ample margins of safety built-in, allowing superior performance while maintaining the machine at top shape for as long as possible.
Reliable Components
A system is only as reliable as its weakest link — or the worse quality component. True Reliability is not obtained via skimming on costs for cheap materials and parts.
04
Dynamic Control Systems
Lightning-Speed
Fast dynamic controls technology is key towards smooth, shocks-free mechanical motions. Interrupt-driven, Hard-Real-Time controls with closed-loop feedback is a must.
Adaptive Intelligence
The prevalence of signal noises, hydraulic spikes, mechanical shocks, temperature fluctuations and normal wear-and-tear means that rigid dynamical systems degrade over time in an not-totally-predictable manner.
In order to maintain stable performance and high precision, misaligned components must be promptly compensated for and brought back into alignment automatically and dynamically through adaptive algorithms.

Related
 Return of the King in CHINAPLAS 2018: Great Success for Chen Hsong April 29, 2018 - Having completed 60 years and making a mark at CHINAPLAS 2018, Chen Hsong is clearly working towards the next 60 years to greater glory.
Return of the King in CHINAPLAS 2018: Great Success for Chen Hsong April 29, 2018 - Having completed 60 years and making a mark at CHINAPLAS 2018, Chen Hsong is clearly working towards the next 60 years to greater glory.  Super Stable and Amazing SPEED (Kayaking Teaser) April 17, 2018 - World-Class Skills for World-Class Results!
Super Stable and Amazing SPEED (Kayaking Teaser) April 17, 2018 - World-Class Skills for World-Class Results!  An Evergreen in The Toys Industry – The Secrets of Wah Lung Toys September 6, 2017 - How Chen Hsong machines let Wah Lung be evergreen.
An Evergreen in The Toys Industry – The Secrets of Wah Lung Toys September 6, 2017 - How Chen Hsong machines let Wah Lung be evergreen.  The Amazing MK6 – 99%+ Yield with Ultra-High Precision August 16, 2016 - Do multi-material over-molding with standard machines only!
The Amazing MK6 – 99%+ Yield with Ultra-High Precision August 16, 2016 - Do multi-material over-molding with standard machines only!